- Home
- Products
- Cables and Cable Compounds
- Power Cables
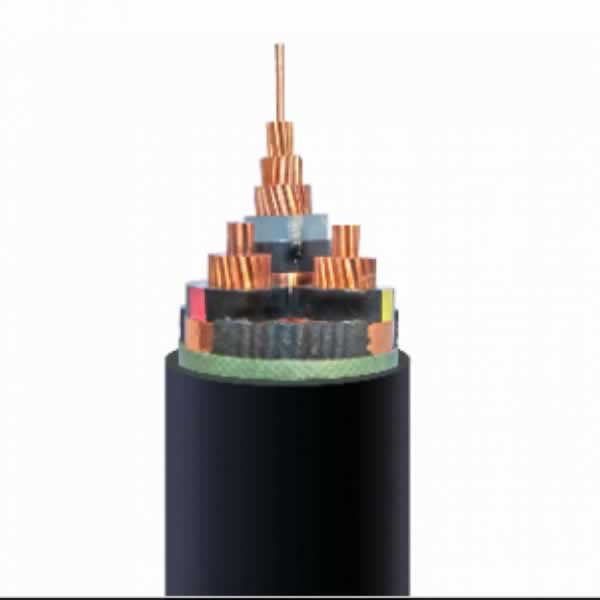
Power Cables
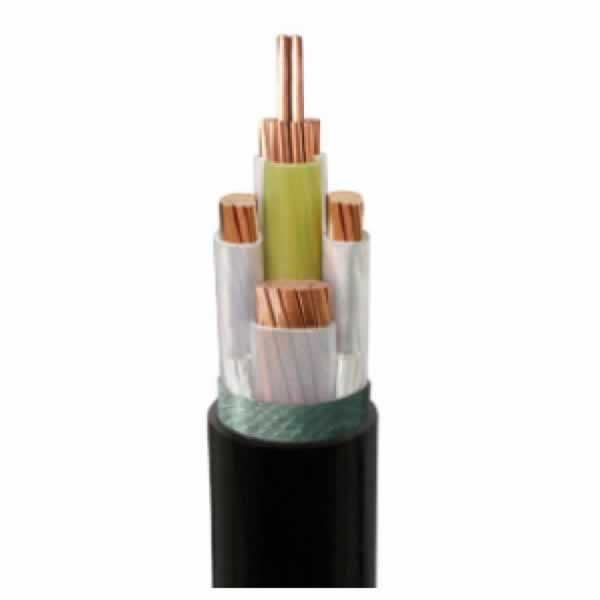
LV XLPE Insulated Unarmored Power Cable
Voltage:0.6/1kV
MV XLPE Insulated Unarmored Power Cable
Voltage:3.6/6, 6/10, 8.7/15, 12/20, 21/35, 26/35kV
21/35kV XLPE Insulated Power Cable
Voltage:26/35kV
21/35kV XLPE Insulated Power Cable
Voltage:21/35kV
18/30kV XLPE Insulated Power Cable
Voltage: 18/30kV
12/20kV XLPE Insulated Power Cable
Voltage: 12/20kV
8.7/15kV XLPE Insulated Power Cable
Voltage: 8.7/15kV
6/10kV XLPE Insulated Power Cable
Voltage: 6/10kV
3.6/6kV XLPE Insulated Power Cable
Voltage: 3.6/6kV
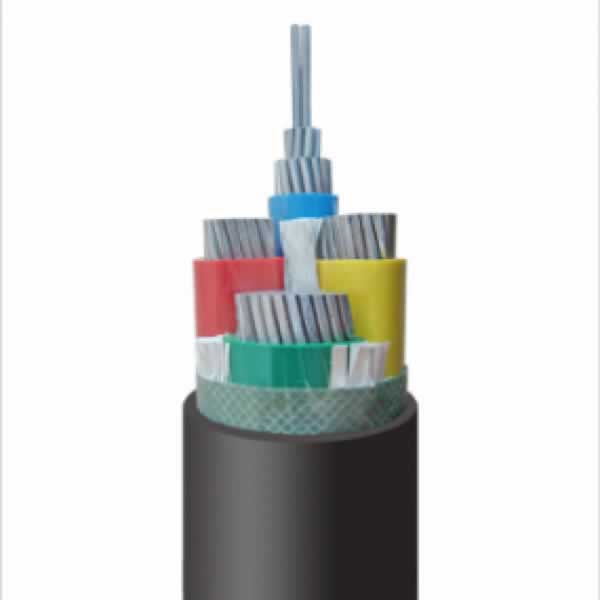
CU/XLPE/SWA/PVC, AL/XLPE/SWA/PVC MV
Voltage: 3.6/6kV, 6/10kV, 8.7/15kV, 12/20kV, 18/30kV, 21/35kV, 26/35kV
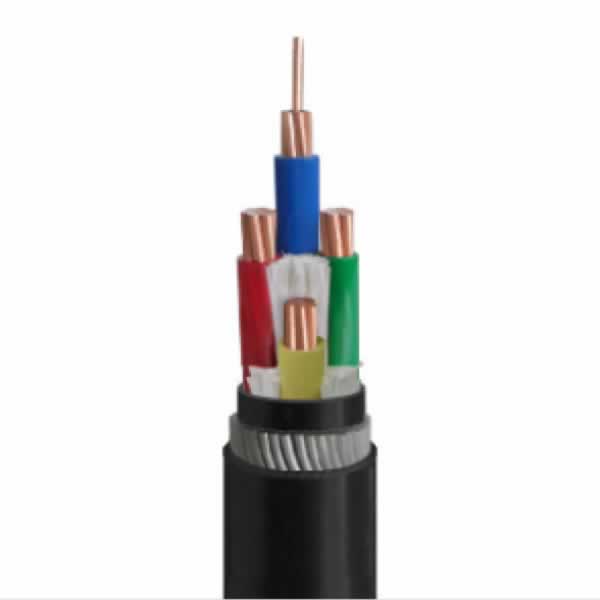
CU/XLPE/SWA/PVC, AL/XLPE/SWA/PVC 0.6/1kV
Voltage: 0.6/1kV
CU/XLPE/STA/PVC, AL/XLPE/STA/PVC MV
Voltage: 3.6/6kV, 6/10kV, 8.7/15kV, 12/20kV, 18/30kV, 21/35kV, 26/35kV
CU/XLPE/STA/PVC, AL/XLPE/STA/PVC 0.6/1kV
Voltage: 0.6/1KV
CU/XLPE/PVC 26/35kV
Voltage: 26/35kV
CU/XLPE/PVC 21/35kV
Voltage: 21/35kV
CU/XLPE/PVC 18/30kV
Voltage: 18/30kV
CU/XLPE/PVC 12/20kV
Voltage: 12/20kV
CU/XLPE/PVC 8.7/15kV
Voltage: 8.7/15kV
CU/XLPE/PVC 6/10kV
Voltage: 6/10kV
CU/XLPE/PVC 3.6/6kV
Voltage: 3.6/6kV
CU/XLPE/PVC Medium Voltage
Voltage: 1.8/3kV, 6/10kV, 8.7/10kV, 8.7/15kV, 12/20kV, 21/35kV, 26/35kV
0.6/1kV XLPE Insulated Power Cable
Voltage: 0.6/1kV
XLPE Insulated Power Cable
Voltage: 0.6/1kV, 1.8/3kV, 6/10kV, 8.7/10kV, 8.7/15kV, 12/20kV, 21/35kV, 26/35kV
CU/XLPE/PVC single-core 0.6/1kV
Voltage: 0.6/1kV
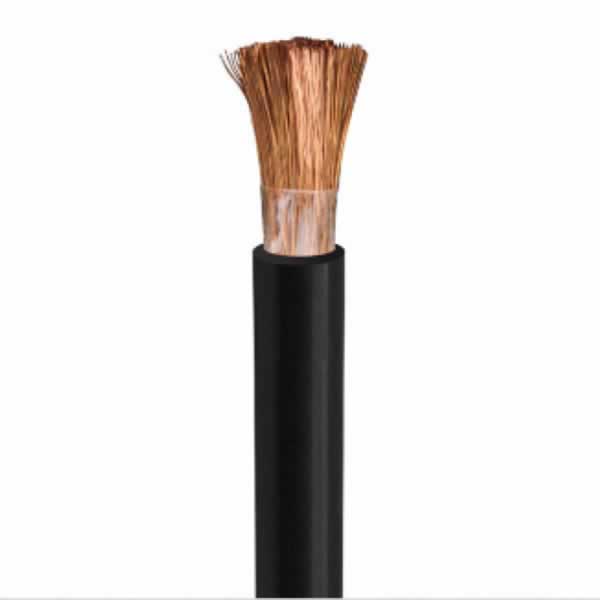
Welding Cable
Voltage:
Standard:IEC 60245-6: 2003, GB5013-2008
Applications:For the transmission of high currents from the electric welding machine to the
welding tool.
CU/PVC/SWA/PVC, AL/PVC/SWA/PVC 0.6/1kV
Voltage:0.6/1kV
CU/PVC/STA/PVC, AL/PVC/STA/PVC 0.6/1kV
Voltage: 0.6/1kV
AL/PVC/PVC 0.6/1kV
Voltage: 0.6/1kV
CU/PVC/PVC 0.6/1kV
Voltage: 0.6/1kV
300/500V Rubber cable for coal mining electric drill
Voltage: 300/500V
Non-metallic shielding flexible rubber cable with monitoring core for movable coal mining machines
Voltage: 8.7/10kV below
Metallic shielding flexible rubber cable with monitoring core for movable coal mining machines
Voltage: 8.7/10kV below
Flexible rubber cable for movable coal mining machines
Voltage: 0.66/1.44kV below
Metallic shielding flexible rubber cable for coal mining machines
Voltage: 1.9/3.3kV below
Flexible rubber cable for coal mining machines
Voltage: 1.9/3.3kV below
Instrument Cable
Voltage:300/500V
Standard:Q/ILXD30.1~4, equal to BS5308-86
Applications:Used in process controls, transmission of signals, computers, control systems and
monitor networks as well as in intrinsically safe systems in hazardous areas like petrochemical
plants and thermal power plants
60227 IEC 07 (International), BV-90 300/500V(China)
Voltage: 300/500V
60227 IEC 08 (International), RV-90 300/500V(China)
Voltage: 300/500V
60227 IEC 01 (International), BV or BVR 450/750V(China)
Voltage: 450/750V
60227 IEC 05 (International), BV 300/500V(China)
Voltage: 300/500V
ABC-Aerial Bundled Cable
Voltage:
Standard: GB12527-91,IEC502, BS7870-5
Applications: aerial bunch cables are a combination of power cables and overhead conductors
Other search items: unarmoured power cables
How to choose high quality Power Cables?
Here are some factors to consider when choosing high-quality power cables:
Conductor Material: Look for cables with high-quality conductor materials such as copper or aluminum, which provide good conductivity and durability.
Insulation Material: Check the type of insulation material used in the cable. High-quality cables typically use materials such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) or rubber that are durable, flexible and have good insulating properties.
Jacket Material: The jacket of the cable is the outer layer that protects it from external elements such as moisture, heat and chemicals. A high-quality cable will have a jacket made from durable and robust materials like nylon or polyurethane.
Current Capacity: Make sure the cable is capable of handling the amount of current that you need it to carry. Check the ampacity rating to ensure that it can handle the electrical load without overheating or failing.
Length: Choose the appropriate length of cable that you need for your application. Longer cables can experience more voltage drop and may require larger conductors to maintain proper voltage levels.
Certification: Look for certifications such as UL, CSA, or ETL to ensure that the cable meets industry standards for quality and safety.
By considering these factors, you can choose a high-quality power cable that will meet your needs and provide reliable power transmission.